Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Canny edge detector#
The Canny filter is a multi-stage edge detector. It uses a filter based on the derivative of a Gaussian in order to compute the intensity of the gradients.The Gaussian reduces the effect of noise present in the image. Then, potential edges are thinned down to 1-pixel curves by removing non-maximum pixels of the gradient magnitude. Finally, edge pixels are kept or removed using hysteresis thresholding on the gradient magnitude.
The Canny has three adjustable parameters: the width of the Gaussian (the noisier the image, the greater the width), and the low and high threshold for the hysteresis thresholding.
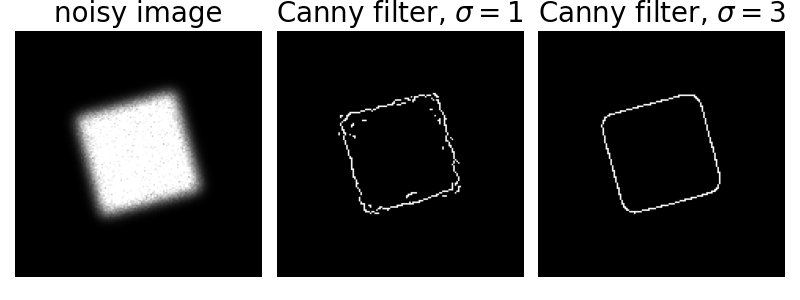
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import ndimage as ndi
from skimage.util import random_noise
from skimage import feature
# Generate noisy image of a square
image = np.zeros((128, 128), dtype=float)
image[32:-32, 32:-32] = 1
image = ndi.rotate(image, 15, mode='constant')
image = ndi.gaussian_filter(image, 4)
image = random_noise(image, mode='speckle', mean=0.1)
# Compute the Canny filter for two values of sigma
edges1 = feature.canny(image)
edges2 = feature.canny(image, sigma=3)
# display results
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=3, figsize=(8, 3))
ax[0].imshow(image, cmap='gray')
ax[0].set_title('noisy image', fontsize=20)
ax[1].imshow(edges1, cmap='gray')
ax[1].set_title(r'Canny filter, $\sigma=1$', fontsize=20)
ax[2].imshow(edges2, cmap='gray')
ax[2].set_title(r'Canny filter, $\sigma=3$', fontsize=20)
for a in ax:
a.axis('off')
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.188 seconds)
