Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Histogram Equalization#
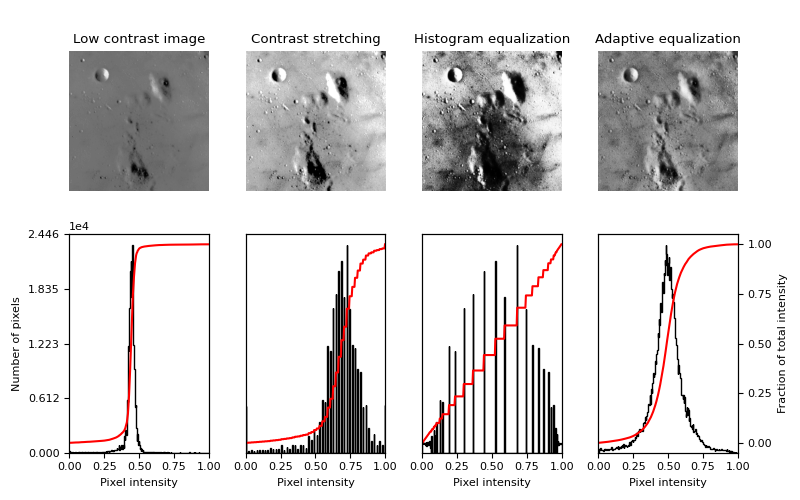
This examples enhances an image with low contrast, using a method called histogram equalization, which “spreads out the most frequent intensity values” in an image [1]. The equalized image has a roughly linear cumulative distribution function.
While histogram equalization has the advantage that it requires no parameters, it sometimes yields unnatural looking images. An alternative method is contrast stretching, where the image is rescaled to include all intensities that fall within the 2nd and 98th percentiles [2].
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from skimage import data, img_as_float
from skimage import exposure
matplotlib.rcParams['font.size'] = 8
def plot_img_and_hist(image, axes, bins=256):
"""Plot an image along with its histogram and cumulative histogram."""
image = img_as_float(image)
ax_img, ax_hist = axes
ax_cdf = ax_hist.twinx()
# Display image
ax_img.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax_img.set_axis_off()
# Display histogram
ax_hist.hist(image.ravel(), bins=bins, histtype='step', color='black')
ax_hist.ticklabel_format(axis='y', style='scientific', scilimits=(0, 0))
ax_hist.set_xlabel('Pixel intensity')
ax_hist.set_xlim(0, 1)
ax_hist.set_yticks([])
# Display cumulative distribution
img_cdf, bins = exposure.cumulative_distribution(image, bins)
ax_cdf.plot(bins, img_cdf, 'r')
ax_cdf.set_yticks([])
return ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf
# Load an example image
img = data.moon()
# Contrast stretching
p2, p98 = np.percentile(img, (2, 98))
img_rescale = exposure.rescale_intensity(img, in_range=(p2, p98))
# Equalization
img_eq = exposure.equalize_hist(img)
# Adaptive Equalization
img_adapteq = exposure.equalize_adapthist(img, clip_limit=0.03)
# Display results
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
axes = np.zeros((2, 4), dtype=object)
axes[0, 0] = fig.add_subplot(2, 4, 1)
for i in range(1, 4):
axes[0, i] = fig.add_subplot(2, 4, 1 + i, sharex=axes[0, 0], sharey=axes[0, 0])
for i in range(0, 4):
axes[1, i] = fig.add_subplot(2, 4, 5 + i)
ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf = plot_img_and_hist(img, axes[:, 0])
ax_img.set_title('Low contrast image')
y_min, y_max = ax_hist.get_ylim()
ax_hist.set_ylabel('Number of pixels')
ax_hist.set_yticks(np.linspace(0, y_max, 5))
ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf = plot_img_and_hist(img_rescale, axes[:, 1])
ax_img.set_title('Contrast stretching')
ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf = plot_img_and_hist(img_eq, axes[:, 2])
ax_img.set_title('Histogram equalization')
ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf = plot_img_and_hist(img_adapteq, axes[:, 3])
ax_img.set_title('Adaptive equalization')
ax_cdf.set_ylabel('Fraction of total intensity')
ax_cdf.set_yticks(np.linspace(0, 1, 5))
# prevent overlap of y-axis labels
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.763 seconds)
