Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Convex Hull#
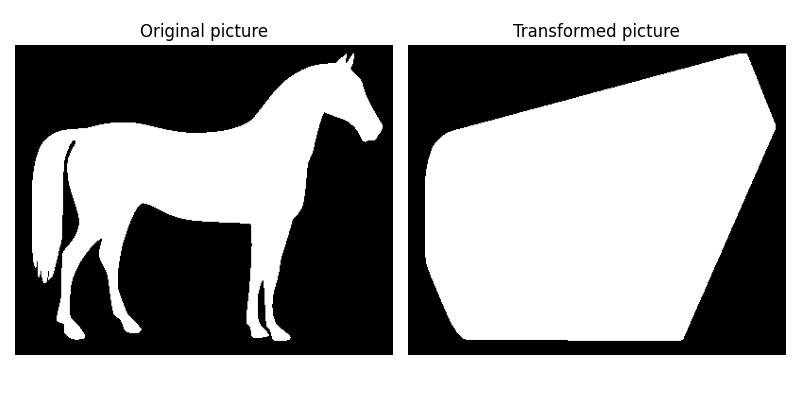
The convex hull of a binary image is the set of pixels included in the smallest convex polygon that surround all white pixels in the input.
A good overview of the algorithm is given on Steve Eddin’s blog.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage.morphology import convex_hull_image
from skimage import data, img_as_float
from skimage.util import invert
# The original image is inverted as the object must be white.
image = invert(data.horse())
chull = convex_hull_image(image)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(8, 4))
ax = axes.ravel()
ax[0].set_title('Original picture')
ax[0].imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[0].set_axis_off()
ax[1].set_title('Transformed picture')
ax[1].imshow(chull, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[1].set_axis_off()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
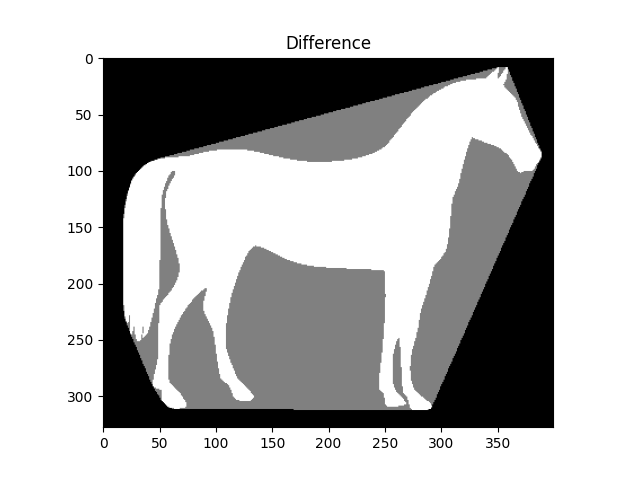
We prepare a second plot to show the difference.
chull_diff = img_as_float(chull.copy())
chull_diff[image] = 2
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.imshow(chull_diff, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax.set_title('Difference')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.546 seconds)